Types of Computer
We can categorize computer in two ways: on the basis of data handling capabilities and size.
On the basis of data handling capabilities, the computer is of three types:
1) Analogue Computer
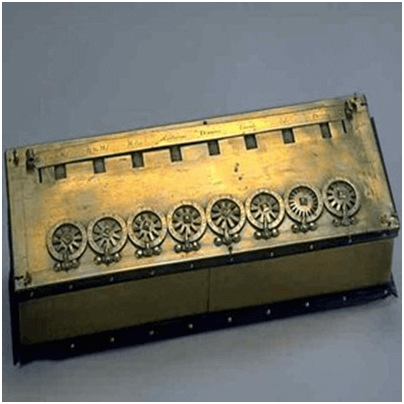
Analogue computers are designed to process analogue data. Analogue data is continuous data that changes continuously and cannot have discrete values. We can say that analogue computers are used where we don't need exact values always such as speed, temperature, pressure and current.
Analogue computers directly accept the data from the measuring device without first converting it into numbers and codes. They measure the continuous changes in physical quantity and generally render output as a reading on a dial or scale. Speedometer and mercury thermometer are examples of analogue computers.
Advantages of using analogue computers:
- It allows real-time operations and computation at the same time and continuous representation of all data within the rage of the analogue machine.
- In some applications, it allows performing calculations without taking the help of transducers for converting the inputs or outputs to digital electronic form and vice versa.
- The programmer can scale the problem for the dynamic range of the analogue computer. It provides insight into the problem and helps understand the errors and their effects.
Types of analogue computers:
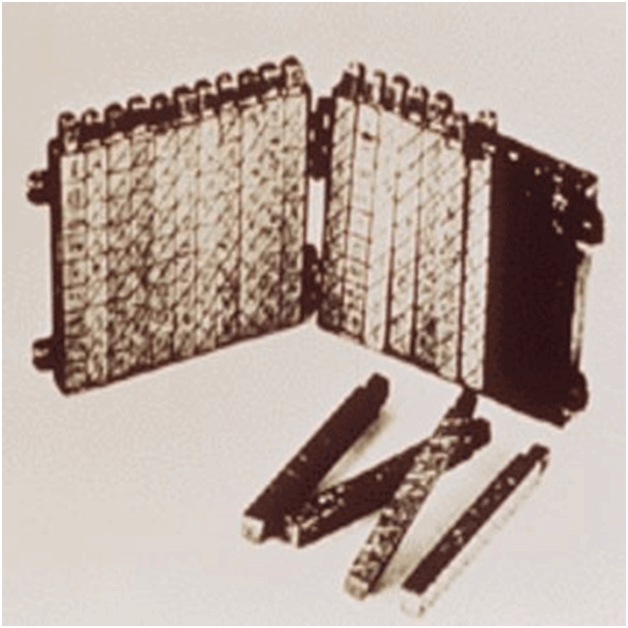
- Slide Rules: It is one of the simplest types of mechanical analogue computers. It was developed to perform basic mathematical calculations. It is made of two rods. To perform the calculation, the hashed rod is slid to line up with the markings on another rod.
- Differential Analysers: It was developed to perform differential calculations. It performs integration using wheel-and-disc mechanisms to solve differential calculations.
- Castle Clock: It was invented by Al-Jarazi. It was able to save programming instructions. Its height was around 11 feet and it was provided with the display of time, the zodiac, and the solar and lunar orbits. This device also could allow users to set the length of the day as per the current season.
- Electronic Analogue Computer: In this type of analogue computer, electrical signals flow through capacitors and resistors to simulate physical phenomena. Here, the mechanical interaction of components does not take place. The voltage of the electrical signal generates the appropriate displays.
2) Digital Computer
Digital computer is designed to perform calculations and logical operations at high speed. It accepts the raw data as input in the form of digits or binary numbers (0 and 1) and processes it with programs stored in its memory to produce the output. All modern computers like laptops, desktops including smartphones that we use at home or office are digital computers.
Advantages of digital computers:
- It allows you to store a large amount of information and to retrieve it easily whenever you need it.
- You can easily add new features to digital systems more easily.
- Different applications can be used in digital systems just by changing the program without making any changes in hardware
- The cost of hardware is less due to the advancement in the IC technology.
- It offers high speed as the data is processed digitally.
- It is highly reliable as it uses error correction codes.
- Reproducibility of results is higher as the output is not affected by noise, temperature, humidity, and other properties of its components.
3) Hybrid Computer
Hybrid computer has features of both analogue and digital computer. It is fast like an analogue computer and has memory and accuracy like digital computers. It can process both continuous and discrete data. It accepts analogue signals and convert them into digital form before processing. So, it is widely used in specialized applications where both analogue and digital data is processed. For example, a processor is used in petrol pumps that converts the measurements of fuel flow into quantity and price. Similarly, they are used in airplanes, hospitals, and scientific applications.
Advantages of using hybrid computers:
- Its computing speed is very high due to the all-parallel configuration of the analogue subsystem.
- It produces precise and quick results that are more accurate and useful.
- It has the ability to solve and manage big equation in real-time.
- It helps in the on-line data processing.
On the basis of size, the computer can be of five types:
1) Supercomputer
Supercomputers are the biggest and fastest computers. They are designed to process huge amount of data. A supercomputer can process trillions of instructions in a second. It has thousands of interconnected processors.
Supercomputers are particularly used in scientific and engineering applications such as weather forecasting, scientific simulations and nuclear energy research. The first supercomputer was developed by Roger Cray in 1976.
Characteristics or applications of supercomputers:
- It has the ability to decrypt your password to enhance protection for security reasons.
- It produces excellent results in animations.
- It is used for virtual testing of nuclear weapons and critical medical tests.
- It can study and understand climate patterns and forecast weather conditions. It can run in NOAA's system (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration) that can execute any type of simple and logical data.
- It helps in designing the flight simulators for pilots at the beginner level for their training.
- It helps in extracting useful information from data storage centres or cloud system. For example, in insurance companies.
- It has played a vital role in managing the online currency world such as stock market and bitcoin.
- It helps in the diagnosis of various critical diseases and in producing accurate results in brain injuries, strokes, etc.
- It helps in scientific research areas by accurately analysing data obtained from exploring the solar system, satellites, and movement of Earth.
- It also used in a smog control system where it predicts the level of fog and other pollutants in the atmosphere.
2) Mainframe computer
Mainframe computers are designed to support hundreds or thousands of users simultaneously. They can support multiple programs at the same time. It means they can execute different processes simultaneously. These features of mainframe computers make them ideal for big organizations like banking and telecom sectors, which need to manage and process high volume of data.
Mainframe computers are designed to support hundreds or thousands of users simultaneously. They can support multiple programs at the same time. It means they can execute different processes simultaneously. These features of mainframe computers make them ideal for big organizations like banking and telecom sectors, which need to manage and process a high volume of data that requires integer operations such as indexing, comparisons, etc.
Characteristics of Mainframe Computers:
- It can process huge amount of data, e.g. millions of transactions in a second in the banking sector.
- It has a very long life. It can run smoothly for up to 50 years after proper installation.
- It gives excellent performance with large scale memory management.
- It has the ability to share or distribute its workload among other processors and input/output terminals.
- There are fewer chances of error or bugs during processing in mainframe computers. If any error occurs it can fix it quickly without affecting the performance.
- It has the ability to protect the stored data and other ongoing exchange of information and data.
Applications of mainframe computers:
- In health care, it enabled hospitals to maintain a record of their millions of patients in order to contact them for treatment or related to their appointment, medicine updates or disease updates.
- In the field of defence, it allows the defence departments to share a large amount of sensitive information with other branches of defence.
- In the field of education, it helps big universities to store, manage and retrieve data related to their courses, admissions, students, teachers, employees and affiliated schools and colleges.
- In the retail sector, the retail companies that have a huge customer base and branches use mainframe computers to handle and execute information related to their inventory management, customer management, and huge transactions in a short duration.
3) Miniframe or Minicomputer
It is a midsize multiprocessing computer. It consists of two or more processors and can support 4 to 200 users at one time. Miniframe computers are used in institutes and departments for tasks such as billing, accounting and inventory management. A minicomputer lies between the mainframe and microcomputer as it is smaller than mainframe but larger than a microcomputer.
Characteristics of miniframe or minicomputer:
- It is light weight that makes it easy to carry and fit anywhere.
- It is less expensive than mainframe computers.
- It is very fast compared to its size.
- It remains charged for a long time.
- It does not require a controlled operational environment.
Applications of minicomputers:
A minicomputer is mainly used to perform three primary functions, which are as follows:
- Process control: It was used for process control in manufacturing. It mainly performs two primary functions that are collecting data and feedback. If any abnormality occurs in the process, it is detected by the minicomputer and necessary adjustments are made accordingly.
- Data management: It is an excellent device for small organizations to collect, store and share data. Local hospitals and hotels can use it to maintain the records of their patients and customers respectively.
- Communications Portal: It can also play the role of a communication device in larger systems by serving as a portal between a human operator and a central processor or computer.
4) Workstation
Workstation is a single user computer that is designed for technical or scientific applications. It has a faster microprocessor, a large amount of RAM and high speed graphic adapters. It generally performs a specific job with great expertise; accordingly, they are of different types such as graphics workstation, music workstation and engineering design workstation.
Characteristics of workstation computer:
- It is a high-performance computer system designed for a single user for business or professional use.
- It has larger storage capacity, better graphics, and more powerful CPU than a personal computer.
- It can handle animation, data analysis, CAD, audio and video creation and editing.
Any computer that has the following five features, can be termed as a workstation or can be used as a workstation.
- Multiple Processor Cores: It has more processor cores than simple laptops or computers.
- ECC RAM: It is provided with Error-correcting code memory that can fix memory errors before they affect the system's performance.
- RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks): It refers to multiple internal hard drives to store or process data. RAID can be of different types, for example, there can be multiple drives to process data or mirrored drives where if one drive does not work than other starts functioning.
- SSD: It is better than conventional hard-disk drives. It does not have moving parts, so the chances of physical failure are very less.
- Optimized, Higher end GPU: It reduces the load on CPU. E.g., CPU has to do less work while processing the screen output.
5) Microcomputer
Microcomputer is also known as a personal computer. It is a general-purpose computer that is designed for individual use. It has a microprocessor as a central processing unit, memory, storage area, input unit and output unit. Laptops and desktop computers are examples of microcomputers. They are suitable for personal work that may be making an assignment, watching a movie, or at office for office work.
Characteristics of a microcomputer:
- It is the smallest in size among all types of computers.
- A limited number of software can be used.
- It is designed for personal work and applications. Only one user can work at a time.
- It is less expansive and easy to use.
- It does not require the user to have special skills or training to use it.
- Generally, comes with single semiconductor chip.
- It is capable of multitasking such as printing, scanning, browsing, watching videos, etc.
FAQs on the Types of Computers
1. What are the Three Main Types of Computers?
On the basis of data handling capabilities, the three main types of computers are:
- Analog computers
- Digital computers
- Hybrid computers
2. What is a Workstation?
A workstation is a kind of computer that can be used for software development, desktop publishing, and creating engineering applications. Although a modest amount of processing power is present in a workstation, it has relatively good graphical capabilities.
3. What do you Understand by the Term Mainframe?
A mainframe is often very expensive and a very large type of computer. These kinds of computers have the potential to support hundreds and even thousands of people in one go. Furthermore, programs can run simultaneously, and concurrent execution is possible in mainframe computers.
4. What are the advantages of Analog computers?
The advantages of Analog computers are that it represents the data within the system's range and enables users for real-time computations. These as well carry out the calculations without using transducers. Analog systems come in different types, such as Hybrid computers, Digital computers, Castlerock, Electronic Analog computers, slide rules, and differential analyzers. Each of these has advantages and drawbacks of its own. Students who need a thorough explanation of each can go through these on Javatpoint website.
5. What are slide rules?
The simplest analog computer system is the slide. It is used to carry out numerous mathematical computations. These are made up of two rods. The rod slides off with the marking on the other rod when there any calculations are made. In contrast, differential calculations are performed using differential analyzers. These operate using a wheel and disc system. Through Javatpoint, where correct explanations are given that are simple for all pupils to understand, they can learn all the concepts easily.
6. What are digital computers?
All logical operations are completed quickly and efficiently by digital computers. They work with digital or binary numbers. One of the numerous benefits of digital computers is that they can store a large amount of data. Digital computers can simply add new functionality. The cost of these computers is quite low, and the data processing is done at high speed. The cost is quite low, and the data processing is done quickly digitally. For further information about the different sorts of computers, students can consult Javatpoint.
7. What are mainframe computers?
The mainframe is a type of computer that can be characterized as an expensive and substantial computer system. This is very powerful as they have the potential to support numerous users at the same time. These also facilitate different program executions. It provides great performance with extensive memory management and has a long lifespan. Another advantage of using a mainframe is that errors are often quite infrequent, but when they do occur, the system automatically corrects them. They also have a wide range of applications.
8. What do you understand about Hybrid computers?
Digital and analog computers are combined in order to create hybrid computers. Although the accuracy and memory are close to digital computers, the speed is similar to analogue computers. Before the process, these kinds of computers take the analogue signals and transform them into digital signals. These are typically used in specialist applications that combine analog and digital data. Hybrid computers have the capability to resolve complicated problems in real-time and contain a very high speed.
9. Which type of computer has two or more processors and it supports 4 to 200 users at one time.
A minicomputer is a multiprocessing computer of medium size. This type of computer has two or more CPUs and can accommodate 4 to 200 users in one go.