CCNA Interview Questions
A list of top frequently asked CCNA interview questions and answers are given below.
1) What is the difference between switch and hub?
| Basis of Comparison | Hub | Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Hub is a networking device that connects the multiple devices to a single network. | A switch is a control unit that turns the flow of electricity on or off in a circuit. |
| Layer | Hubs are used at the physical layer. | Switches are used at the data link layer. |
| Transmission type | Transmission type can be unicast, broadcast or multicast. | Initially, the transmission type is broadcast and then is unicast. |
| Ports | Hub has 4/12 ports. | The switch has 24/48 ports. |
| Transmission mode | Half duplex | Half/Full duplex. |
| Collisions | Collisions occur commonly in a Hub. | No collisions occur in a full duplex switch. |
| Address used for data transmission | Hub uses MAC address for data transmission. | The switch uses a MAC address for data transmission. |
| Data transmission form | Electrical signal is a data transmission form of a hub. | A Frame is a data transmission form of a switch. |
2) What is the difference between Switch and Router?
| Basis of Comparison | Router | Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Description | It is a layer 3 device that connects the two different networks and identifies the network devices based on their IP addresses. | It is a layer 2 device and determines the network devices based on their MAC addresses. |
| Mode of transmission | Router transmits the data in the form of packets. | Switch transmits the data in the form of frames. |
| Address used | It uses an IP address for the data transmission. | It uses a MAC address to transmit the data. |
| Layer of OSI model | It uses Layer 3 OSI model and layer is the network layer. | It uses layer 2 OSI model and layer is the data link layer. |
| Table | It uses a routing table for routes to move to the destination IP. | It uses a Content address memory table for MAC addresses. |
| Network used | It is used for WAN and LAN networks. | It is used only for LAN networks. |
| Mode of transmission | Router is used in a full-duplex mode. | A switch is used in half as well as in a full-duplex mode. |
3) What are the advantages of using Switches?
Advantages of using Switches:
- Switches are used to receive a signal and create a frame out of the bits from that signal. The signals enable you to get access and read the destination address and after reading that it forward that frame to appropriate frame. So, switches are the significant part of the transmission.
4) What is Routing?
- Routing is a process of finding a path to transfer data from source to destination.
- Routing can be performed in a variety of networks such as circuit switched networks and computer networks.
- In packet switching networks, routing makes a decision that directs the packets from source to the destination.
- Routing makes use of a routing table, which maintains the routes of various destinations.
Types of routing:
- Static routing: Static routing is a routing technique where an administrator manually adds the routes in a routing table. Static routes are used when the route selections are limited. Static routes can also be used in those situations where the devices are fewer and no need to change in the route configuration in future.
- Dynamic routing: Dynamic routing is a routing technique where protocols automatically update the information of a routing table.
5) What are Routers?
- The devices known as Routers do the process of routing. Routers are the network layer devices.
- The router is a networking device which is used to transfer the data across the networks, and that can be wired or wireless.
- Routers use headers and routing table to determine the best route for forwarding the packets.
- Router analyzes the data which is being sent over the network, changes how it is packaged and send it over the network.
Examples of routers are:
- Brouter: Brouter stands for "Bridge Router". It serves both as a router and bridge.
- Core router: Core router is a router in the computer network that routes the data within a network, but not between the networks.
- Edge router: An edge router is a router that resides at the boundary of a network.
- Virtual router: A virtual router is a software-based router. The virtual router performs the packet routing functionality through a software application. A Virtual Router Redundancy protocol implements the virtual router to increase the reliability of the network.
- Wireless router: A wireless router is a router that connects the local networks with another local network.
6) What is the advantage of VLAN?
VLAN is a custom network which is created from one or more existing LAN's. VLAN facilitates you to create a collision domain by groups other than just physical location while in conventional LAN domains are always tied to physical location.
Advantage of VLAN:
- Broadcast control: A VLAN (Virtual Area Network) removes the physical layer and, it logically separates the networks within networks creating a smaller broadcast domain. It reduces the size of the broadcast domain, therefore, improving the efficiency of the network.
- Simplified administration: When a computer is moved to another location, but it stays on the same VLAN without any hardware configuration.
- Security:
- LAN segmentation: Virtual Area Networks are used to logically separate layer 2 switch networks. Users on different VLAN cannot communicate with each other. Therefore, it's a great way of segmentation and provides security.
- Dynamic VLANs: The Dynamic VLAN's are created using the software. The VLAN Management Policy Server (VMPS) is an administrator that dynamically allocates the switch ports based on the information available such as the MAC addresses of the device.
- Protocol-based VLANs: The switch that depends on the protocol based VLANs, then the traffic will be segregated by a particular protocol.
7) What is HDLC?
- HDLC stands for High-Level Data Link Control protocol. It is the property protocol of Cisco which is the default encapsulation operated with Cisco routers.
- HDLC adds the information in a data frame that allows the devices to control the data flow.
- HDLC is a bit-oriented protocol that supports both half and full duplex communication.
- HDLC offers flexibility, adaptability, reliability, and efficiency of operation for synchronous data communication.
- It supports both point-to-point and point-to-multipoint communication.
- It supports synchronous as well as asynchronous communication.
- It provides full data transparency, i.e., the output delivered has the same bit sequence as the input without any restriction.
8) What are the advantages of LAN switching?
LAN switching: LAN switching enables the multiple users to communicate with each other directly. LAN switching provides the collision-free network and high-speed networking.
Following are the main advantages of LAN switching:
- Increased network scalability: LAN switching can handle the increasing amount of work. Therefore, we can say that when the business grows, the network can expand easily.
- Improved bandwidth performance: We require higher bandwidth performance when users operate multimedia applications or some database interactions.
- Multiple simultaneous connections: LAN switching allows multiple simultaneous connections, i.e., it can transfer the multiple data at the same time. This cannot be possible in the case of a hub-based network.
- Reduced congestion and transmission delay: LAN switching improves the performance of a network as a segmented network consists of fewer hosts per subnetwork and thus, minimizing the local traffic.
- No single point of failure: LAN switching provides the proper network designing. Therefore, there are fewer chances of network failure.
- Allows full duplex data transmission: LAN switching allows full duplex data transmission, i.e., the data can be transferred in a bidirectional line at the same time.
9) What is DLCI?
DLCI stands for Data Link Connection Identifiers. These are normally assigned by a frame relay service provider to identify each virtual circuit that exists on the network uniquely.
10) What are the different types of networks?
These are the two major types of networks:
1. Peer-to-Peer Network:
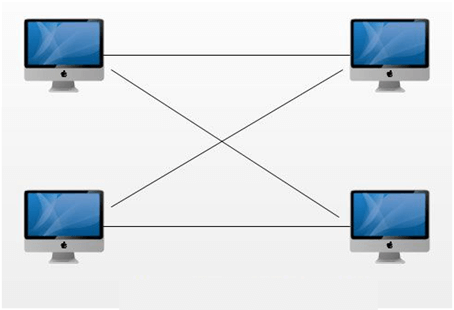
- In a peer-to-peer network, 'peers' are the computers which are connected to each other through an internet connection.
- The computer systems on the network without the need for any computer server.
- Therefore, the computer in P2P is a "computer server" as well as a "client".
- Requirements for a computer to have a peer-to-peer network are the internet connection and P2P software.
- Some of the common P2P software peers include Kazaa, Limewire, BearShare, Morpheus, and Acquisition.
- Once we are connected to the P2P network, then we able to search the files on other people's computer.
Types of a peer-to-peer network:
- Pure P2P: In P2P, peers act as a client and server. There is no central server and central router present in the pure P2P.
- Hybrid P2P: Hybrid P2P has a central server that stores the information and responds to the request for that information. Peers are used for hosting the information as a central server does not store the files. Nasper is an example of Hybrid P2P.
- Mixed P2P: Mixed P2P is a combination of pure P2P and Hybrid P2P.
2. Server-based Network
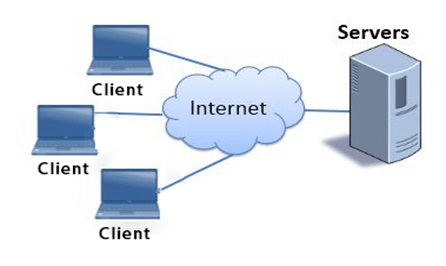
- In a server-based network, server act as a base for the network known as a central server.
- The central server handles multiple tasks such as authenticating users, storing files, managing printers, and running applications such as database and email programs.
- In case of a server-based network, security is centralized in the system which allows the user to have one login id and password to log on to any computer system.
- Server-based networks are more complex and costly and often requires full- time services for administration.
- In server-based networks, the majority of traffic occurs between the servers.
11) What is the difference between private IP and public IP?
Following are the differences between public IP address and private IP address:
| Basis of Comparison | Public IP address | Private IP address |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | It is used for the identification of a home network to the outside world. | It is used for the identification of a network device within the home network. |
| Uniqueness | Public IP address is unique throughout the network. | Private IP address can be the same of two different networks assigned to different computers. |
| Example | 202.60.23.1 | 192.168.0.3 |
| Usage | It is used over the internet or other WAN. | This type of address can be used on a local area network or for the computers that are not connected to the internet. |
| Communication | Public IP address is routable. Therefore, communication among different users is possible. | Private IP address is not routable. Thus, communication among different users is not possible. |
12) What is the difference among straight cable, cross cable and rollover cable?
Straight cable:
- Straight cable is used to connect different group devices. For example Switch- Router.
- Straight cable is a kind of twisted pair cable used in a local area network to connect a computer to a network hub such as a router.
- Straight cables are used for linking different devices.
- It is an 8 wired patch cable.
- It is also used for connecting PC to the switch or router to a hub.
- The main purpose of a straight cable is to connect a host to the client.
Cross cable:
- Cross cable is used to connect the same group devices. For example Switch-Switch.
- Cross cable is a cable used to interconnect two computers by reversing their respective pin contacts.
- Cross cable is a cross-wired cable used to connect the two computers or hosts directly.
- Cross cable is used when two similar devices are to be connected.
- Cross cable crisscross each other, and this makes the communication of two devices at the same time.
Rollover cable:
- Rollover cable is used to connect the console port to the computer.
- Rollover cable is used to connect the computer's terminal to the network's router console port.
- Rollover cable is referred to as a Cisco console cable, and it is flat and light blue in color.
- Another name of a rollover cable is Yost cable.
- Rollover cable is identified by comparing the end of the cable with another cable as rollover cables are beside each other.
- Rollover cable allows the programmer to connect to the network device and can manipulate the programming whenever required.
13) What is the difference between tracert and traceroute?
Differences between tracert and traceroute
| Basis of Comparison | tracert | traceroute |
|---|---|---|
| Description | The tracert command is a command prompt command used to show the route that the packet takes to move from the source to the destination whatever we specify. | The traceroute command is a command used to show the route from your computer to the destination that you specify. |
| Device used | The tracert command is used on pc. | The traceroute command is used on a router or switch. |
| Operating system | The tracert command is used in Windows NT based OS. | The traceroute command is used in UNIX OS. |
14) Explain the terms Unicast, Multicast, Broadcast.
Unicast:
- It specifies one to one communication.
- It is a communication technique in which data communication takes place between two devices present in the network.
- Consider an example of browsing the internet. When we sent a request for some page to the web server, then the request directly goes to the web server to locate the address of a requested page. Therefore, this is one to one communication between client and server.
- Downloading the files from the FTP server is also the best example of unicast communication.
Multicast:
- It specifies one to group communication.
- It is a communication technique in which data communication takes place between a group of devices.
- Multicast uses IGMP(Internet Group Management Protocol) protocol to identify the group.
- Consider an example of video conferencing. If any user in a particular group can initiate the call and the people belongs to this group can participate in this call.
- Sending e-mail to a particular mailing group can also be considered as the example of multicast communication.
Broadcast:
- It specifies one to all communication.
- It is a communication technique in which data communication takes place among all the devices available in the network.
- Broadcasting can be achieved in two ways:
- By using a high-level standard, i.e., Message passing interface. It is an interface used for exchanging the messages between multiple computers.
- By using a low-level standard, i.e., broadcasting through an ethernet.
- Network is not secure in broadcasting as it can lead to a data loss if intruders attack the network.
15) What is the difference between cross cable and straight cable?
Cross cables are used to connect the same group devices while straight cables are used to connect different group devices.
For example: If you want to connect one PC to another PC, you have to use cross cable while, to connect one switch to a router, you have to use a straight cable.
16) What is the difference between static IP addressing and dynamic IP addressing?
Following are the differences between static IP addressing and dynamic IP addressing:
| Basis of Comparison | Static IP address | Dynamic IP address |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Static IP address is a fixed number assigned to the computer. | The dynamic IP address is a temporary number assigned to the computer. |
| Provided By | Static IP address is provided by ISP(Internet Service Provider). | The dynamic IP address is provided by DHCP(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol). |
| Change requirement | It is static means that IP address does not change. | It is non-static means that IP address changes whenever the user connects to a network. |
| Security | It is not secure as IP address is constant. | It is secure because each time IP address changes. |
| Cost | It is costlier than Dynamic IP address. | It is cheaper than the Static IP address. |
| Device tracking | Static IP address is trackable as IP address is constant. | The dynamic IP address is untraceable as IP address is always changing. |
17) What is the difference between CSMA/CD and CSMA/CA?
CSMA/CD stands for Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection. It is a media access control method used in local area networking using early Ethernet technology to overcome the occurred collision.
CSMA/CA stands for Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance. It is used in the wireless network to avoid the collision.
Following are the differences between CSMA/CD and CSMA/CA:
| CSMA/CD | CSMA/CA |
|---|---|
| Full form of CSMA/CD is carrier sense multiple access with collision detection. | Full form of CSMA/CA is carrier sense multiple access with carrier avoidance. |
| CSMA/CD detects the collision, and once the collision is detected, then it stops continuing the data transmission. | CSMA/CA does not deal with the recovery of the collision. |
| Wired installation is used in a CSMA/CD to detect the collision. | Wireless installation is used in a CSMA/CA as it avoids the collision. Therefore, it does not need a wired network. |
| An 802.3 Ethernet network uses CSMA/CD. | An 802.11 ethernet network uses CSMA/CA. |
| CSMA/CD takes effect after the occurrence of a collision. | CSMA/CA takes effect before the occurrence of a collision. |
18) What is the purpose of Data Link Layer?
The main purpose of the data link layer is to check that whether messages are sent to the right devices. Another function of the data link layer is framing.
19) What is VLAN?
VLAN stands for Virtual Local Area Network.
20) What is the subnet? Why is it used?
Subnets are used in IP network to break up the larger network into the smaller network. It is used to optimize the performance of the network because it reduces traffic by breaking the larger network into smaller networks. It is also used to identify and isolate network's problem and simplify them.
21) What is the difference between communication and transmission?
Communication is a process of sending and receiving data from an externally connected data cable whereas transmission is a process of transmitting data from source to destination.
22) What is Topology in CCNA?
Topology is an arrangement of various elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a computer network in a specific order. These are the different types of topology used in CCNA:
Bus:
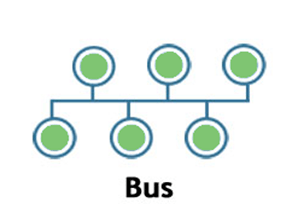
- Bus topology is a network topology in which all the nodes are connected to a single cable known as a central cable or bus.
- It acts as a shared communication medium, i.e., if any device wants to send the data to other devices, then it will send the data over the bus which in turn sends the data to all the attached devices.
- Bus topology is useful for a small number of devices. As if the bus is damaged then the whole network fails.
Star:
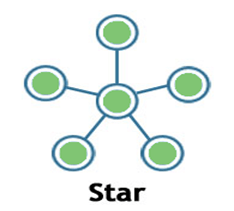
- Star topology is a network topology in which all the nodes are connected to a single device known as a central device.
- Star topology requires more cable compared to other topologies. Therefore, it is more robust as a failure in one cable will only disconnect a specific computer connected to this cable.
- If the central device is damaged, then the whole network fails.
- Star topology is very easy to install, manage and troubleshoot.
- Star topology is commonly used in office and home networks.
Ring:
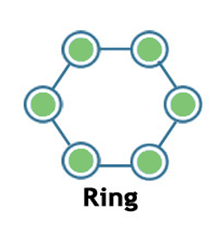
- Ring topology is a network topology in which nodes are exactly connected to two or more nodes and thus, forming a single continuous path for the transmission.
- It does not need any central server to control the connectivity among the nodes.
- If the single node is damaged, then the whole network fails.
- Ring topology is very rarely used as it is expensive, difficult to install and manage.
- Examples of Ring topology are SONET network, SDH network, etc.
Mesh:
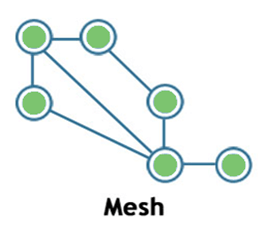
- Mesh topology is a network topology in which all the nodes are individually connected to other nodes.
- It does not need any central switch or hub to control the connectivity among the nodes.
- Mesh topology is categorized into two parts:
- Fully connected mesh topology: In this topology, all the nodes are connected to each other.
- Partially connected mesh topology: In this topology, all the nodes are not connected to each other.
- It is a robust as a failure in one cable will only disconnect the specified computer connected to this cable.
- Mesh topology is rarely used as installation and configuration are difficult when connectivity gets more.
- Cabling cost is high as it requires bulk wiring.
Tree:
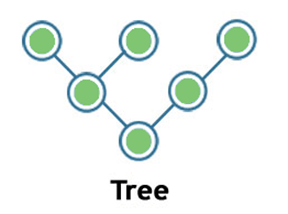
- Tree topology is a combination of star and bus topology. It is also known as the expanded star topology.
- In tree topology, all the star networks are connected to a single bus.
- Ethernet protocol is used in this topology.
- In this, the whole network is divided into segments known as star networks which can be easily maintained. If one segment is damaged, but there is no effect on other segments.
- Tree topology depends on the "main bus," and if it breaks, then the whole network gets damaged.
Hybrid:
- A hybrid topology is a combination of different topologies to form a resulting topology.
- If star topology is connected with another star topology, then it remains star topology. If star topology is connected with different topology, then it becomes a Hybrid topology.
- It provides flexibility as it can be implemented in a different network environment.
- The weakness of a topology is ignored, and only strength will be taken into consideration.
23) What is the passive topology in CCNA?
When the topology enables the computers on the network only to listen and receive the signals, it is known as passive topology because they don't amplify the signals anyway.
24) What is RAID in CCNA?
RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks. RAID is a method which is used to standardize and categorize fault-tolerant disk systems. RAID levels provide various facilities like performance, cost, reliability, etc. These three are the mostly used RAID levels:
- Level 0: (Striping)
- Level 1: (Mirroring)
- Level 5: (Striping and Parity)
25) What is the point-to-point protocol in CCNA?
The point-to-point protocol is an industry standard suite of protocols which uses the point-to-point link to transport multiprotocol datagram. The point-to-point protocol is a WAN protocol used at layer 2 to encapsulate the frames for the data transmission over the physical layer.
Following are the features that point-to-point protocol provides:
- Link quality management: It is a technique to monitor the quality of a link. If it finds any error in a link, then the link is shut down.
- The point-to-point protocol also provides authentication.
- It provides some essential features such as authentication, error detection, link quality monitoring, load balancing, compression, etc.
Components of a point-to-point protocol are:
- Encapsulation: Point-to-point protocol encapsulates the network packets in its frames using HDLC protocol. This makes the PPP layer three layer independent.
- Link Control Protocol: Link Control Protocol is used for establishing, configuring and testing the data link over internet connections.
- Network Control Protocol: Point-to-point protocol is used in a data link layer in the OSI reference model. The data comes from the upper layer, i.e., transport layer or network layer is fully compatible with PPP due to the presence of a Network control protocol.
26) What are the possible ways of data transmission in CCNA?
Simplex, half-duplex and full-duplex are the communication channels used to convey the information. Either the communication channel can be a physical medium or logical medium.
These are the three possible ways of data transmission:
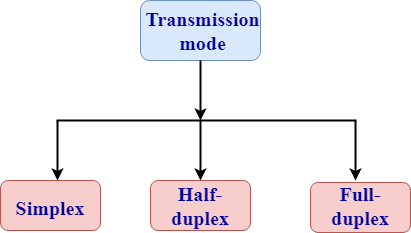
Simplex

- The simplex communication channel sends the data only in one direction.
- Example of the simplex communication channel is a radio station. The radio station transmits the signal while the other receives the signal.
- In simplex mode, entire bandwidth can be utilized for the data transmission as a flow of data is in one direction.
Half-duplex
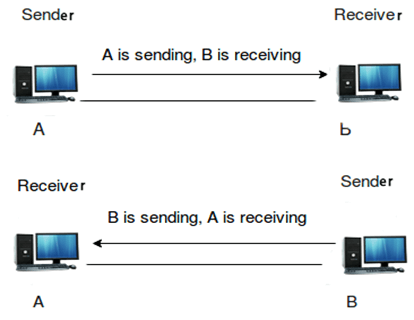
- The half-duplex communication channel sends the information in both the directions but not at the same time.
- Performance of half-duplex is better than the simplex communication channel as the data flows in both the directions.
- Example of the half-duplex communication channel is "walkie-talkie". In "walkie-talkie", both the transmitter and receiver can communicate with each other on the same channel.
- In half-duplex mode, entire bandwidth can be used by the transmitter when the message is sent over the communication channel.
Full-duplex
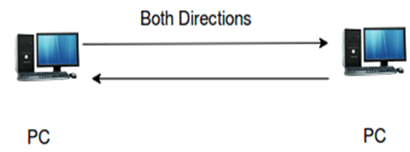
- The full-duplex communication channel can send the information in both the directions at the same time.
- Performance of full-duplex is better than the half-duplex communication channel as the data flows in both the direction at the same time.
- Example of a full-duplex communication channel is "telephone". In the case of telephone, one can speak and hear at the same time. Therefore, this channel increases the efficiency of communication.
27) What are the protocol data units (PDU) in CCNA?
Protocol data units (PDU) are the minimum possible units used at different layers of the OSI model to transport data.
| Layers | PDU |
|---|---|
| Transport | Segments |
| Network | Packets/Datagrams |
| Data-link | Frames |
| Physical | Bits |
28) What is the difference between RIP and IGRP?
Following are the differences between RIP and IGRP:
| Basis of Comparison | RIP | IGRP |
|---|---|---|
| Full form | RIP stands for routing information protocol. | IGRP stands for interior gateway routing protocol. |
| Description | RIP is a distance vector-based routing protocol. | IGRP is a distance vector based interior gateway routing protocol. |
| Determination of route | RIP depends on the number of hops to determine the best route to the network. | IGRP considers many factors before decides the best route to take, i.e., bandwidth, reliability, MTU and hops count. |
| Standard | RIP is a industry standard dynamic protocol. | IGRP is a Cisco standard dynamic protocol. |
| Organization used | RIP is mainly used for smaller sized organizations. | IGRP is mainly used for medium to large-sized organizations. |
| Maximum routers | It supports maximum 15 routers. | It supports a maximum 255 routers. |
| Symbol used | RIP is denoted by 'R' in the routing table. | IGRP is denoted by 'I' in the routing table. |
| Administrative distance | The administrative distance of RIP is 120. | The administrative distance of IGRP is 100. |
| Algorithm | RIP works on Bellman ford Algorithm. | IGRP works on Bellman ford Algorithm. |
29) What are the different memories used in a CISCO router?
Three types of memories are used in a CISCO router:
- NVRAM
- NVRAM stands for Non-volatile random access memory.
- It is used to store the startup configuration file.
- NVRAM retains the configuration file even if the router shut down.
- DRAM
- DRAM stands for dynamic random access memory.
- It stores the configuration file that is being executed.
- DRAM is used by the processor to access the data directly rather than accessing it from scratch.
- DRAM is located near the processor that provides the faster access to the data than the storage media such as hard disk.
- Simple design, low cost, and high speed are the main features of DRAM memory.
- DRAM is a volatile memory.
- Flash Memory
- It is used to store the system IOS.
- Flash memory is used to store the ios images.
- Flash memory is erasable and reprogrammable ROM.
- The capacity of the flash memory is large enough to accommodate many different IOS versions.
30) What is the difference between full-duplex and half-duplex?
Following are the differences between half-duplex and full-duplex
| Basis of Comparison | Half-duplex | Full-duplex |
|---|---|---|
| Direction of communication | Communication is bi-directional but not at the same time. | Communication is bi-directional and done at the same time. |
| Send/receive | A sender can send as well as receive the data but not at the same time. | A sender can send as well as receive the data simultaneously. |
| Performance | Performance of half-duplex mode is not as good as a full-duplex mode. | Performance of full-duplex mode is better than the half-duplex mode. |
| Example | Example of half-duplex is a walkie-talkie. | Example of full-duplex is a telephone. |
31) What is BootP?
BootP is a short form of Boot Program. It is a protocol that is used to boot diskless workstation connected to the network. BootP is also used by diskless workstations to determine its IP address and also the IP addresses of server PC.
32) What is a Frame Relay?
Frame Relay is used to provide connection-oriented communication by creating and maintaining virtual circuits. It is a WAN protocol that is operated at the Data Link and physical layer to sustain high-performance rating.
How frame relay works.
Frame relay multiplexes the traffic coming from different connections over a shared physical medium using special purpose hardware components such as routers, bridges, switch that packages the data into a frame relay messages. It reduces the network latency, i.e., the number of delays. It also supports the variable sized packet for the efficient utilization of network bandwidth.
33) What is Latency?
Latency is the amount of time delay. It is measured as the time difference between at the point of time when a network receives the data, and the time it is sent by another network.
34) What is the MAC address?
MAC address stands for Media Access Control address. This is an address of a device which is identified as the Media Access Control Layer in the network architecture. The MAC address is unique and usually stored in ROM.
35) What is the difference between ARP and RARP?
ARP stands for Address Resolution Protocol. ARP is a protocol that is used to map an IP address to a physical machine address.
RAPR stands for Reverse Address Resolution Protocol. RARP is a protocol that is used to map a MAC address to IP address.
Following are the differences between ARP and RARP:
| Basis of Comparison | ARP | RARP |
|---|---|---|
| Full form | Full form of ARP is address resolution protocol. | Full form of RARP is reverse address resolution protocol. |
| Description | ARP contains the logical address, and it retrieves the physical address of the receiver. | RARP includes the physical address and retrieves the logical address of a computer from the server. |
| Mapping | ARP is used to map 32-bit logical address to 48-bit physical address. | RARP is used to map 48-bit physical address to 32-bit logical address. |
36) What is the size of an IP address?
The size for IPv4 is 32 bits and 128 bits for IPv6.
37) What is Ping? What is the usage of Ping?
PING stands for Packet Internet Groper. It is a computer network tool which is used to test whether a particular host is reachable across an IP address or not.
38) What is the checksum?
The checksum is a simple error detection scheme in which each transmitted message is accompanied by a numerical value based on the number of set bits in the message.
39) What are the different types of the password used in securing a Cisco router?
There are five types of passwords can be set on a Cisco router:
- Consol
- Aux
- VTY
- Enable Password
- Enable Secret
40) What is the usage of Service Password Encryption?
Service Password Encryption command is used to encrypt all passwords on your router to hide from your running config.













0 Comments:
Post a Comment
Need Help ? Make A Comment Below & We'll Help You Out ?.....:)